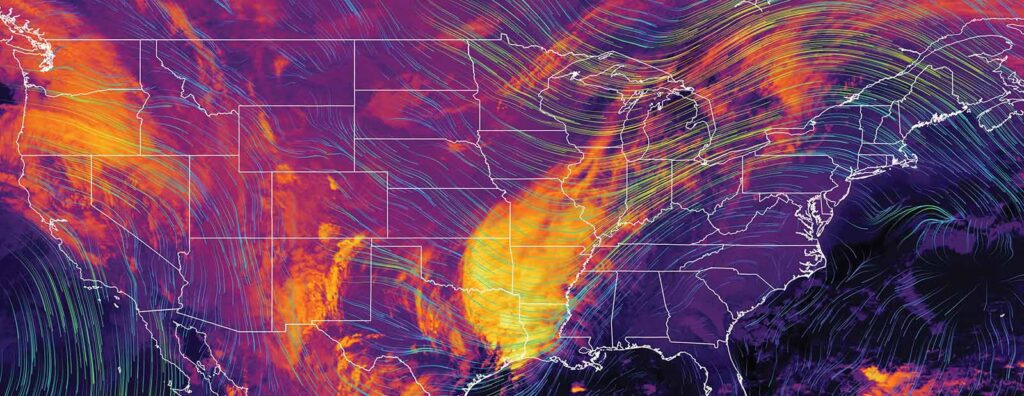
We are told that global temperature is rising, yet millions nationwide are feeling the Arctic chill from repeated winter storms. It is a paradox: Does global warming affect winter? It does. First, it is essential to distinguish between ‘weather’ and ‘climate.’ Weather represents short-term atmospheric conditions in a specific area, while climate is the average of these conditions over extended periods. This distinction is key in understanding current weather patterns, including the cold wave, within the broader context of climate change.
El Niño and Jet Stream Patterns: Unpredictable Weather Catalysts
Recent weather phenomena can be partly attributed to the intricate workings of El Niño and jet stream patterns. El Niño, a climate pattern in the Pacific Ocean, impacts global weather. It typically brings warmer temperatures; however, its interaction with the jet stream, a high-altitude air current, can lead to unexpected outcomes, such as sudden drops in temperature in certain regions. This interaction exemplifies the complexity of atmospheric dynamics and its unpredictable impact on local weather conditions. And that is what we are experiencing now.
Moreover, climate change is intensifying these phenomena. Warmer air holds more moisture, leading to heavier precipitation in various forms, including snow. A warming Arctic is also believed to influence the jet stream, making it wavier and sluggish. This results in prolonged weather patterns, whether they be heatwaves or cold spells.
Case Study: Arctic Influence on North American Winters
In a recent issue of National Geographic, Arctic air is increasingly reaching southern latitudes, and North America can expect to see harsher winters. That was the conclusion of a study published in 2017 in the journal Nature Geoscience. It found a link between warmer Arctic temperatures and colder North American winters.”
“Warm temperatures in the Arctic cause the jet stream to take these wild swings, and when it swings farther south, that causes cold air to reach farther south. These swings tend to hang around for a while, so the weather we have in the eastern United States, whether it’s cold or warm, tends to stay with us longer,” said study author Jennifer Francis in a press release.
Implications for Emergency Preparedness and Policy
Understanding El Niño, climate change, and the unpredictable dynamics of jet stream patterns is essential for government staff and emergency managers because the future of extreme weather points toward more frequent, intense, and varied locations of hurricanes, floods, droughts, wildfires, and heatwaves The major implication of increased frequency and severity of extreme weather events leads to a higher demand for emergency services and an increased strain on existing infrastructure. Governments and organizations must adapt their emergency preparedness plans to account for these changes to effectively respond to disasters.
Another implication is the potential shift in disaster-prone areas due to changing climate patterns. For example, areas once considered low risk for hurricanes may become more vulnerable due to rising sea levels and warmer ocean temperatures. This requires a reassessment of evacuation plans and other disaster management strategies.
Moreover, El Nino events can also cause indirect impacts such as food shortages and water scarcity. Droughts can reduce crop yields, leading to food insecurity in affected regions. This can also result in conflicts over resources and displacement of populations.
In policy, governments must incorporate climate change considerations into their emergency preparedness plans to mitigate its impacts. This includes investing in early warning systems, improving infrastructure resilience, implementing land-use planning strategies to reduce vulnerability in high-risk areas, and promoting disaster risk reduction measures.
Furthermore, with the increasing occurrence of severe natural disasters driven by El Nino and climate change, there is a growing need for international cooperation in emergency response efforts. This includes sharing resources and expertise among countries that are impacted by similar disasters.
Preparedness for such extremes requires accepting the nuanced relationship between climate and weather. It’s not just about expecting hotter summers but also bracing for colder winters and more variable weather patterns, so governments will need to re-evaluate their policies and emergency plans to address these challenges and protect vulnerable communities from the devastating effects of natural disasters exacerbated by these phenomena.
Adapting to a Changing Climate
The current frigid temperatures remind us of the complex and sometimes counterintuitive ways climate change impacts our weather. As we navigate this new era, continuous research and adaptive strategies will be vital in managing the challenges of an ever-changing climate.
On an individual level, people can contribute by embracing sustainable practices such as reducing carbon emissions, conserving energy, and adopting eco-friendly lifestyles. This can include using renewable energy sources, practicing water conservation, and supporting green initiatives.
At the governmental level, policies and regulations that promote sustainability and climate resilience are crucial. Governments can invest in renewable energy infrastructure, enforce stricter emissions standards, and incentivize businesses to adopt sustainable practices. Collaboration between nations is also essential to address global challenges posed by climate change.
By taking these steps and working collectively, we can better adapt to the impacts of climate change and safeguard our planet for future generations.