Updated for 2025 hurricane season
This article has been reviewed and expanded with the latest information on spaghetti models, including updated interpretation tips, modern forecasting tools, and current best practices for hurricane preparedness.
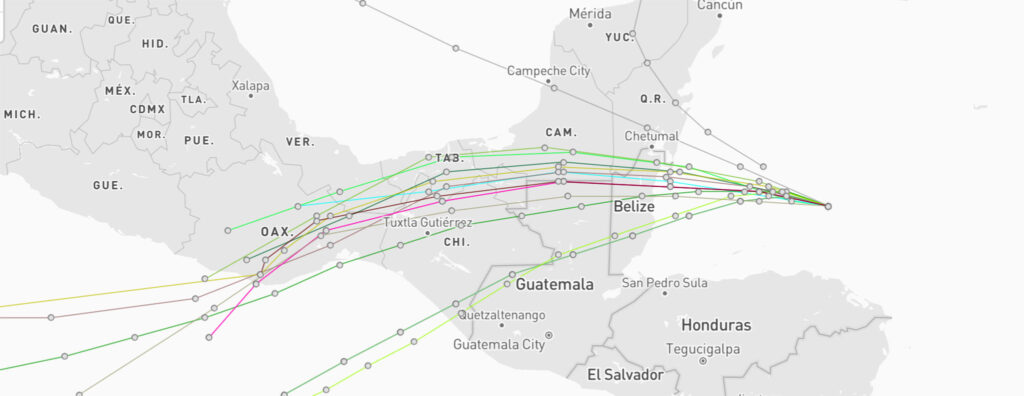
Spaghetti models are weather forecasting maps that display multiple possible paths of a storm, most often used during hurricane season. Each line in the model represents a different forecast run based on varying data inputs, creating a tangled “spaghetti-like” appearance. These unique models provide a visual representation of possible trajectories for weather systems, particularly hurricanes, offering insights that can guide emergency response efforts. In this article, we explore the intricacies of spaghetti models, their historical development, and their application in hurricane season.
What Are Spaghetti Models?
Spaghetti models, often seen during hurricane season, are a series of lines plotted on a map, each representing a potential path of a storm. These models derive their name from the tangled appearance of the lines of data, reminiscent of a plate of spaghetti. They are generated by computer simulations that use meteorological data to project the potential movement of a storm. Each line, or “ensemble member,” represents a different model’s prediction based on various initial conditions and assumptions.
The Importance of Spaghetti Models in Storm Forecasting
The primary function of spaghetti models is to convey the range of possible storm paths, emphasizing uncertainty rather than a single projected track. This visual tool helps meteorologists communicate to the public and emergency managers the inherent variability in storm predictions, while highlighting areas that may be affected.
Visual representation is a key aspect of spaghetti models. The overlapping lines showcase a range of outcomes, assisting forecasters in identifying the most likely path a storm may take. By analyzing these models, experts can recognize trends and refine their predictions, making them an indispensable resource during hurricane season.
In addition to path predictions, spaghetti models can provide information on storm intensity, speed, and duration. This comprehensive data allows governments, emergency managers, and community members to make informed decisions about evacuations, resource allocation, and communication strategies and improve their preparedness and response efforts.
History of Spaghetti Models
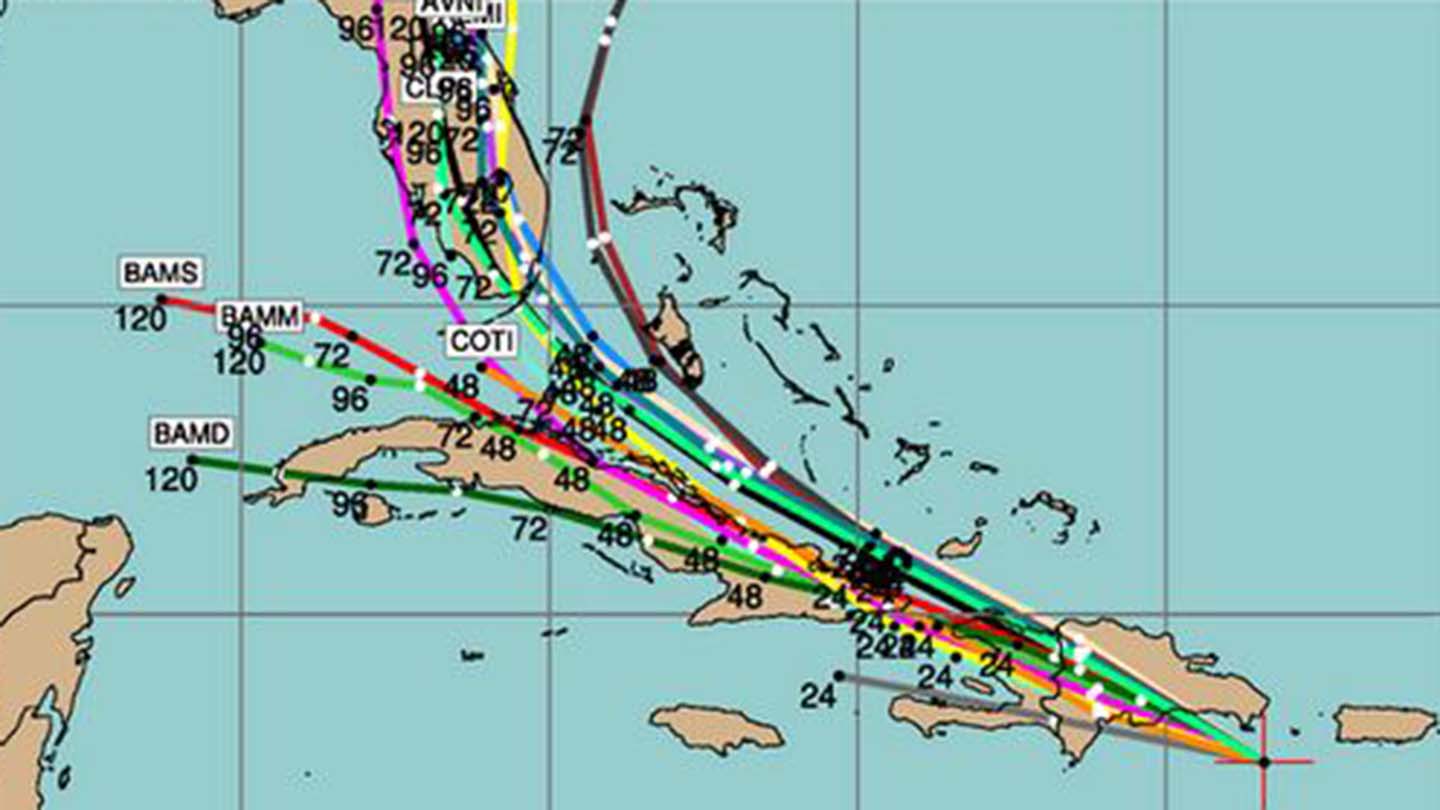
The development of spaghetti models is rooted in the evolution of meteorological science and computing technology. In the early days of weather forecasting, predictions were primarily based on simple models and observational data. With advancements in computing power and the advent of numerical weather prediction (NWP), the ability to simulate atmospheric conditions improved significantly.
The concept of ensemble forecasting, which forms the basis of spaghetti models, emerged in the 1960s and 1970s. Scientists recognized that small variations in initial conditions could lead to vastly different outcomes, necessitating multiple simulations to capture the range of possible scenarios. This approach laid the groundwork for modern spaghetti models.
Over the decades, spaghetti models have evolved alongside advancements in computational capabilities and meteorological research. The introduction of supercomputers and sophisticated algorithms has enabled meteorologists to generate more accurate and detailed models, refining their ability to predict storm behavior.
One significant milestone in the history of spaghetti models was the development of the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) ensemble prediction system in the 1980s. This system introduced the concept of probabilistic forecasting, providing a more comprehensive view of uncertainty in weather predictions. Today, ECMWF remains a leading institution in ensemble forecasting, contributing to the accuracy and reliability of spaghetti models worldwide.
Another notable advancement came with the integration of satellite data into weather models. Satellites offer real-time observations of atmospheric conditions, enhancing the accuracy of initial inputs and improving the overall quality of spaghetti models. This integration has revolutionized forecasting, allowing meteorologists to track storms with unprecedented precision.
Current Spaghetti Models
Modern spaghetti models in 2025 continue to leverage advanced numerical weather prediction systems, real-time satellite observations, and high-resolution radar data to forecast storm paths with greater accuracy than ever before. This year, meteorologists are benefiting from several key advancements:
- Higher-Resolution Ensemble Forecasting – Upgrades to systems like the ECMWF and GFS have improved map resolution, allowing for more precise tracking of subtle shifts in storm direction.
- Expanded Data Sources – New weather buoys and aerial reconnaissance flights provide more frequent and detailed measurements of wind speed, pressure, and sea surface temperatures.
- Artificial Intelligence Integration – Machine learning models are now assisting meteorologists by spotting historical pattern matches that can refine track and intensity predictions.
- Faster Update Cycles – With 2025’s increased computational power, ensemble runs can be processed and published more often, giving emergency managers and the public faster access to updated paths.
These improvements mean that today’s spaghetti models are more accurate and more responsive to sudden changes in storm behavior. During the 2025 hurricane season, expect more reliable early warnings and more detailed probability maps that help decision-makers prepare with greater confidence.
How Spaghetti Models Are Used in Hurricane Season

During the hurricane season, spaghetti models become important tools for meteorologists, emergency managers, and the public. Understanding how to interpret these models can help them make informed decisions about safety and preparedness.
When a tropical cyclone forms, spaghetti models quickly become part of the forecasting toolbox. They offer a visual representation of the potential paths, helping forecasters identify areas at risk. This information helps them issue timely warnings and evacuation orders.
Interpreting Spaghetti Models for Effective Decision-Making
Understanding spaghetti models is one way we can make informed decisions during storm predictions. These models can be complex, but breaking them down into key components can enhance their utility. Here are three ways to interpret spaghetti models:
- Consider Model Limitations: Spaghetti models focus on predicting the storm’s center path, often neglecting impacts like rainfall or wind. This is crucial when a storm’s severity isn’t accurately reflected by its path.
- Evaluate Model Consistency: Confidence in forecasts increases when multiple models and runs show similar results. Consistency suggests stable conditions or a well-understood situation.
- Use Ensembles for Long-Range Forecasting: Ensembles, or multiple runs with slight variations, are key for medium to long-term forecasting. When ensemble members cluster closely, confidence is higher; divergence indicates higher uncertainty.
Frequently Asked Questions about Spaghetti Models
- How do spaghetti models differ from traditional weather forecasts?
Spaghetti models focus on illustrating potential storm paths through ensemble forecasting, while traditional forecasts often present a single predicted track. This approach emphasizes the uncertainty in storm predictions and offers a more comprehensive view of possible outcomes. - Why do spaghetti models show different paths for the same storm?
Each line in a spaghetti model represents a different simulation based on varying initial conditions and assumptions. The differences in paths highlight the inherent uncertainty in storm predictions, helping meteorologists communicate the range of potential outcomes. - Can spaghetti models predict storm intensity?
Yes, spaghetti models can provide information on storm intensity, speed, and duration. These additional data points help emergency managers make informed decisions about evacuations, resource allocation, and communication strategies. - Are spaghetti models used for weather events other than hurricanes?
While spaghetti models are commonly associated with hurricanes, they can be used for other weather events, such as winter storms and tropical cyclones. The principles of ensemble forecasting apply to various types of storms, providing valuable insights for decision-makers. - How accurate are spaghetti models compared to other forecasting methods?
Spaghetti models offer a probabilistic approach to forecasting, which can provide a more comprehensive view of uncertainty compared to deterministic forecasts. While no forecasting method is infallible, ensemble forecasting has proven effective in capturing the range of possible outcomes. - How do spaghetti models account for changes in storm behavior?
Spaghetti models continuously update with new data, incorporating real-time observations and refined initial conditions. This iterative process allows meteorologists to track changes in storm behavior and adjust their predictions accordingly. - How do meteorologists ensure the reliability of spaghetti models?
Meteorologists validate spaghetti models through extensive testing and comparison with observed weather patterns. By refining algorithms and incorporating new data sources, they continuously improve the accuracy and reliability of these models. - Can individuals access spaghetti models to inform personal preparedness efforts?
While spaghetti models are primarily used by meteorologists and emergency managers, some sources, such as the National Hurricane Center, provide access to these models for public viewing. Individuals can use this information to stay informed and make informed decisions about their personal safety. - How do spaghetti models contribute to post-disaster recovery efforts?
Spaghetti models help assess the accuracy of predictions and evaluate the effectiveness of response strategies, informing future preparedness efforts and improving community resilience. - Are there any limitations to the use of spaghetti models in disaster preparedness?
While spaghetti models provide valuable insights, they are subject to uncertainty and should be used in conjunction with other forecasting tools and expert judgment. Decision-makers must consider the full range of available information when planning for disaster response. - How can spaghetti models be used to educate the public about storm risks?
By sharing spaghetti models through various media channels, meteorologists can emphasize the uncertainty in storm predictions and encourage individuals to prepare for a range of outcomes. - What resources are available for learning more about spaghetti models?
The National Hurricane Center and other meteorological institutions provide educational resources on spaghetti models and their application in disaster preparedness. Additionally, reputable news sources and scientific publications offer insights into the latest developments in ensemble forecasting.
Strengthening Disaster Preparedness with Spaghetti Models
Spaghetti models play a vital role in modern disaster preparedness. They offer a comprehensive view of potential storm paths and aid decision-makers in planning effective response strategies. By understanding the intricacies of these models and their applications, individuals and communities can enhance their resilience in the face of natural disasters.
Our team is available to provide personalized support and resources for disaster preparedness. Reach out to us today to learn how we can assist you in navigating hurricane season and beyond.